
Just west of Hood River is a distinctive, short (<500 m) section of stratified orangeish oxidized volcanic tephra and highly fractured lava bombs. This mixture of oxidized volcanic particles ranging down to sub-micrometer sizes mixed with the larger lava bombs is a palagonite tuff.

This deposit is the result of a “phreatic” eruption when lava erupted explosively from a volcanic vent through water, like a lake or groundwater. The rapid heating expansion of water to steam blew the rising lava out of the vent as tephra (volcanic rock fragments) ranging from ash-size to volcanic bombs (blobs of lava) up to several inches in diameter. Rapid oxidation of the water-quenched tephra turned the iron content to rust, producing the orangeish color of the tephra. The lava bombs were heavily fractured due to rapid cooling of the blob as it came in contact with the water and as it flew through the air.
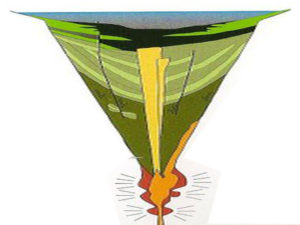
The tephra deposits dip inward on either side of a central gap toward the gap, with NE dips in the western section and NW dips in the eastern section, forming an inverted cone that converges downward toward the central gap.
This feature is a “maar” deposit; an inverted cone of tephra and lava resulting from rapidly rising magma interacting with groundwater causing a steam-driven explosive eruption that builds the surrounding maar. The vent of this maar was in the area of the central gap.